Micro injection molding is a tight precision molding technology used to produce minimal parts and components. In the medical business, micromolded elements are employed for surgical instruments and other purposes. Micro molding technology is also widely used in telecommunications and other sectors where the industry trend towards "smaller is better" persists.
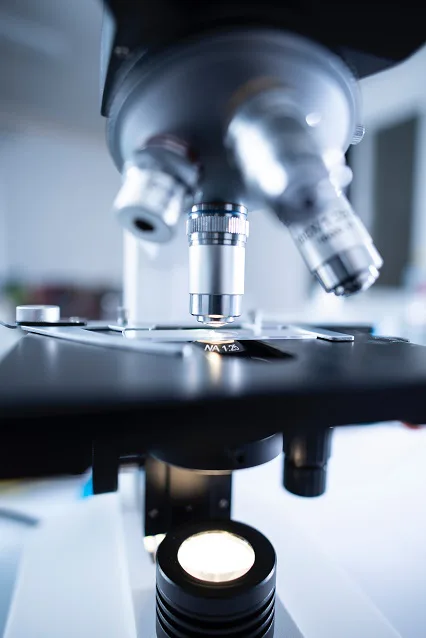

One of the more complex injection molding procedures is micro molding. By nature, the polymers utilized have "large" molecules. Since these molecules behave differently than when used in more extensive applications, it can be difficult to work with them at the small measurements required for micro injection molding. While strict tolerances are required for all injection molding processes, dimensional errors, even at the smallest scale, can render parts of this size useless.
Plastic injection molding is a method of producing plastic objects of varied sizes, intricacy, and applicability. A vertical or horizontal injection molding press, a mold, and raw plastic resin are required for the procedure. The injection molding machine melts the plastic resin substance, which is then fed into the mold, where it cools and hardens into the final part or pieces.

Before diving into the procedure of micro injection molding, it is essential to know the materials used in the process. Polypropylene, Polycarbonate, Polysulfone, Nylon (Polyamide), Polyethylene, and Delrin( acetyl or POM), are common materials used for micro molding Polybutylene terephthalate, Acrylic – Polymethylmethacrylate and PMMA.
Stages Of Micromolding
Moving forward, Clamping, Injection, Cooling, and Ejection are the four main stages of the procedure.
Injection Molding Machine- Clamping Unit
Each side of the injection mold is clamped to the injection molding machine through the clamping unit. While the liquefied resin material is injected into the mold cavities, the motorized clamping mechanism presses the mold halves together and exerts considerable strength to keep the mold securely closed.
The time necessary to lock and shut the mold depends on the molding press size. Clamping is one factor to consider when determining the size of the injection molding press needed to produce your product. Once you know the size press your item demands, you'll know one element your injection molder requires to achieve your item.
Resin Raw Material- Injection Phase
When the raw material is injected, it is fed into the injection molding press and pushed toward the mold by the injection unit. High temperature and pressure cause the raw resin material to melt during the progression. The injection device takes the molten plastic and holds it in the chambers of the mold using force packs.
A collection of parameters, such as the barrel temperature, nozzle temperature, and injection mold, must be used to achieve correct melt temperatures. The quality of plastics throughout the mold is affected by the barrel and nozzle temperatures—mold temperature influences both circulation through the mold and the freezing of the molded component.
The temperatures selected for the barrel and nozzle should be evaluated carefully. Very high-temperature results in overflow and explosion, whereas temperatures adjusted too low lead to empty sections.
Another aspect of injection molding is plastic pressure. It refers to the physical force imparted to the molten resin by the screw head as the screw travels ahead, a process regulated by the injection molding press's automated system.
When building a stable injection molding process, pressure and temperature are two components that must be controlled.
Plastic Injection Molding- Cooling Period
The molten plastic inside the mold cavities will harden into the shape of the item as it cools. Cooling starts inside the mold the moment it comes into touch with the inner mold surfaces. The mold will not be able to be opened until the required cooling period has passed.
The injection mold temperature should be set according to the guidelines provided by the resin raw material supplier. The cooling times are influenced by the design of the part and mold, as well as the resin raw material utilized. Internal cooling is built into the injection mold layout.
Plastic Part Ejection
After the requisite cooling period has expired, the part is ejected. An ejection mechanism forces the component(s) out when the clamping unit unlocks the injection mold. The part shrinks and sticks to the mold cavities throughout the cooling process, necessitating pressure to expel the item.
Following ejection and retrieval of portions or parts, the mold closes in preparation for the injection of the next round, initiating the next cycle.
Ways To Look After Your Micromolding Lab
Micromolding labs deal with expensive machinery and substances. It is necessary to take measures for their safety. Install surveillance systems that support live telecasting similar to a ptz camera for church live streaming.
If you choose to keep firearms for personal protection in the lab, keep them inside gun safe vaults. Mishandling of guns can cause a lot of damage.
The Takeaway
The entire process is complex, and it requires highly trained individuals to oversee it. To manufacture micron-tolerance components and devices, tooling and plastics engineers must apply years of experience and teamwork. In this way, percentage tolerance risks are estimated accurately and methods to mitigate them are identified at each phase of the process. A micro molding project's success depends on the steps within each phase.











0 comments